Ruby arrays are ordered collections of objects. They can hold objects like integer, number, hash, string, symbol or any other array.
Its indexing starts with 0. The negative index starts with -1 from the end of the array. For example, -1 indicates last element of the array and 0 indicates first element of the array.
Creating Ruby Arrays
A Ruby array is created in many ways.
- Using literal constructor []
- Using new class method
Using literal construct []
A Ruby array is constructed using literal constructor []. A single array can contain different type of objects.
For example, following array contains an integer, floating number and a string.
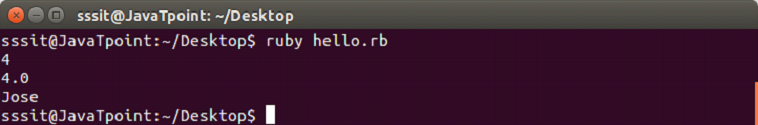
exm = [4, 4.0, "Jose", ]
puts exmOutput:
Using new class method
A Ruby array is constructed by calling ::new method with zero, one or more than one arguments.
Syntax:
- arrayName = Array.new
To set the size of an array,
Syntax:
- arrayName = Array.new(10)
Here, we have mentioned that array size is of 10 elements.
To know the size of an array, either size or length method is used.
Example:
#!/usr/bin/ruby
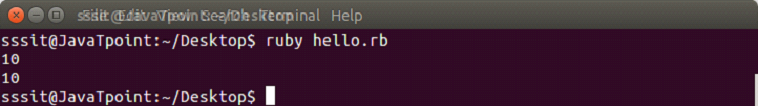
exm = Array.new(10)
puts exm.size
puts exm.lengthOutput:
Example:
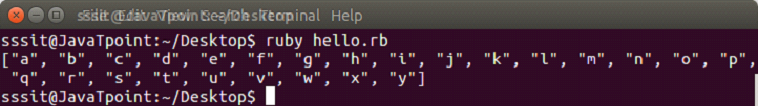
#!/usr/bin/ruby
exm = Array("a"..."z")
puts "#{exm}"Output:
Accessing Array Elements
Ruby array elements can be accessed using #[] method. You can pass one or more than one arguments or even a range of arguments.
#[] method Example:
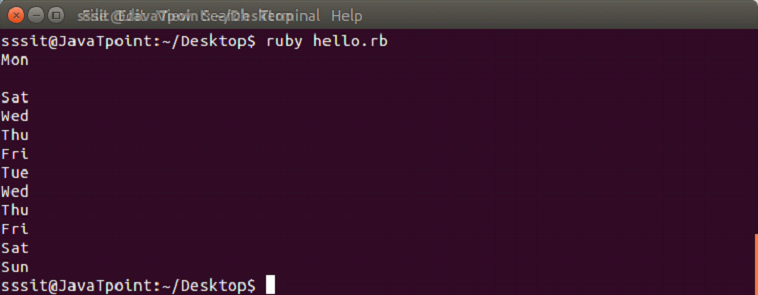
days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days[0]
puts days[10]
puts days[-2]
puts days[2, 3]
puts days[1..7]Output:
at method
To access a particular element, at method can also be used.
Example:
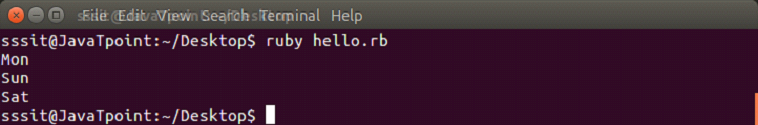
days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.at(0)
puts days.at(-1)
puts days.at(5)Output:
slice method
The slice method works similar to #[] method.
fetch method
The fetch method is used to provide a default value error for out of array range indices.
Example:
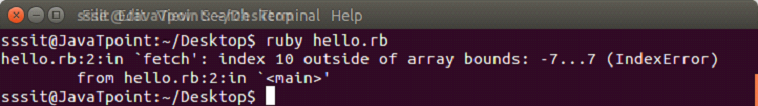
- days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
- puts days.fetch(10)
Output:
Example:
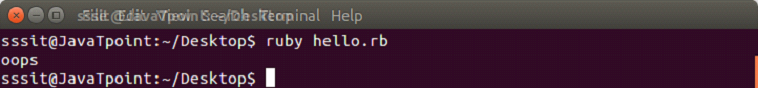
days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.fetch(10, "oops")Output:
first and last method
The first and last method will return first and last element of an array respectively.
Example:
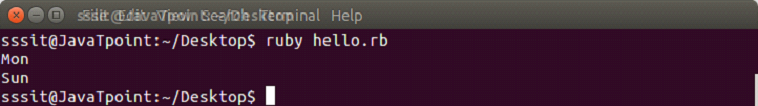
days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.first
puts days.lastOutput:
take method
The take method returns the first n elements of an array.
Example:
days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.take(1)
puts days.take(2)Output:
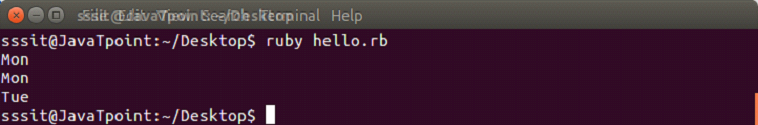
drop method
The drop method is the opposite of take method. It returns elements after n elements have been dropped.
Example:
days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.drop(5)
puts days.drop(6)days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.drop(5)
puts days.drop(6)Output:
Adding Items to Array
Ruby array elements can be added in different ways.
- push or <<
- unshift
- insert
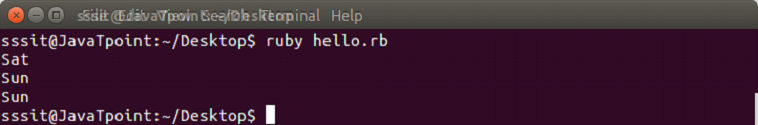
push or <<
Using push or <<, items can be added at the end of an array.
Example:
days = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.push("Today")
puts days << ("Tomorrow")Output:
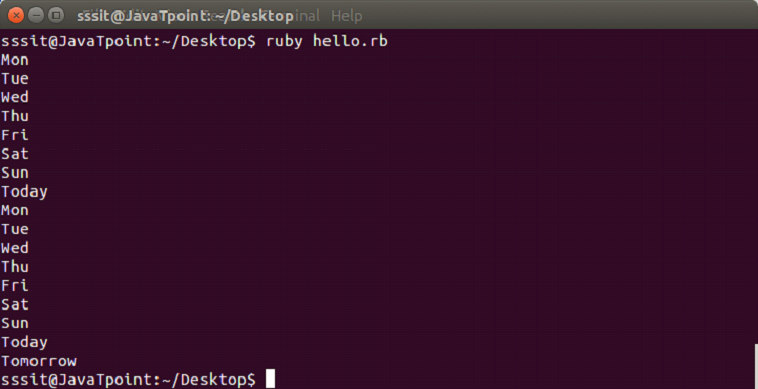
unshift
Using unshift, a new element can be added at the beginning of an array.
Example:
days = ["Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.unshift("Today")Output:
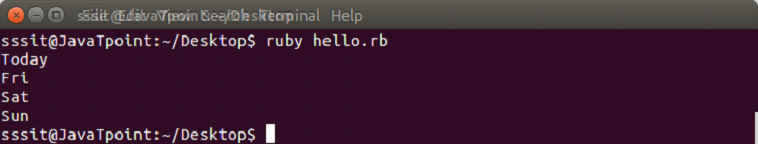
insert
Using insert, a new element can be added at any position in an array. Here, first we need to mention the index number at which we want to position the element.
Example:
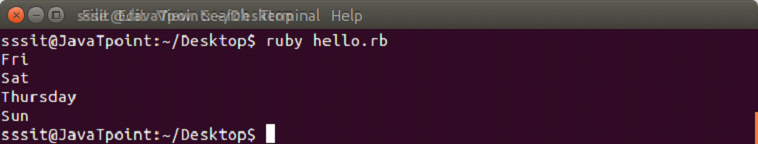
days = ["Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.insert(2, "Thursday")Output:
Removing Items from Array
Ruby array elements can be removed in different ways.
- pop
- shift
- delete
- uniq
pop
Using pop, items can be removed from the end of an array. It returns the removed item.
Example:
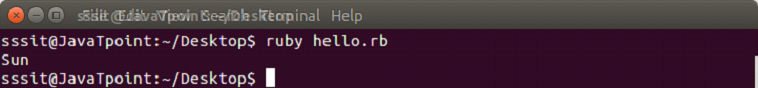
days = ["Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.popOutput:
shift
Using shift, items can be removed from the start of an array. It returns the removed item.
Example:
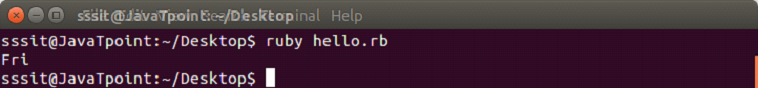
- days = ["Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
- puts days.shift
Output:
delete
Using delete, items can be removed from anywhere in an array. It returns the removed item.
Example:
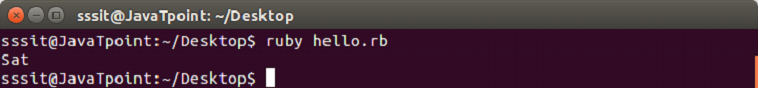
days = ["Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
puts days.delete("Sat")Output:
uniq
Using uniq, duplicate elements can be removed from an array. It returns the remaining array.
Example:
days = ["Fri", "Sat", "Sun", "Sat"]
puts days.uniq
Leave a Reply