Ruby range represents a set of values with a beginning and an end. They can be constructed using s..e and s…e literals or with ::new.
The ranges which has .. in them, run from beginning to end inclusively. The ranges which has … in them, run exclusively the end value.
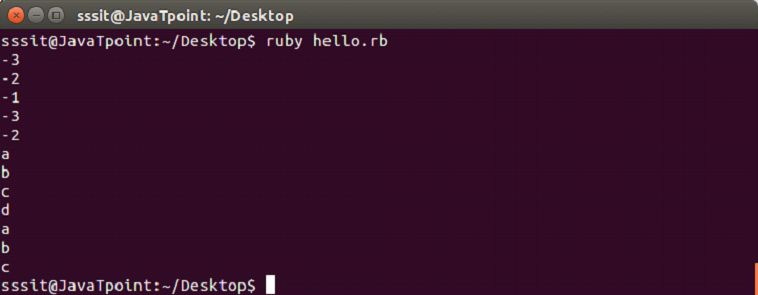
puts (-5..-1).to_a
puts (-5...-1).to_a
puts ('a'..'e').to_a
puts ('a'...'e').to_aOutput:
Ruby has a variety of ways to define ranges.
- Ranges as sequences
- Ranges as conditions
- Ranges as intervals
Ranges as Sequences
The most natural way to define a range is in sequence. They have a start point and an end point. They are created using either .. or … operators.
We are taking a sample range from 0 to 5. The following operations are performed on this range.
Example:
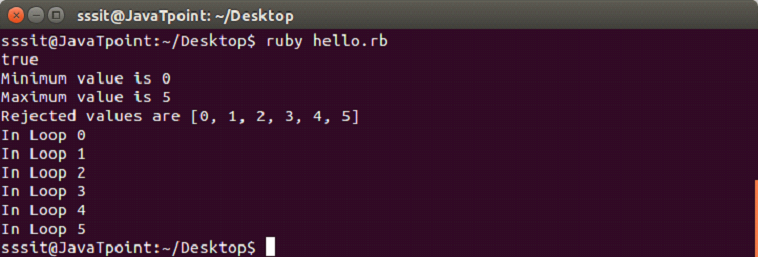
- #!/usr/bin/ruby
-
- range = 0..5
-
- puts range.include?(3)
- ans = range.min
- puts "Minimum value is #{ans}"
-
- ans = range.max
- puts "Maximum value is #{ans}"
-
- ans = range.reject {|i| i < 5 }
- puts "Rejected values are #{ans}"
-
- range.each do |digit|
- puts "In Loop #{digit}"
- end
Output:
Ranges as Conditions
Ranges are also defined as conditional expressions. Different conditions are defined in a set of lines. These conditions are enclosed within start statement and end statement.
Example:
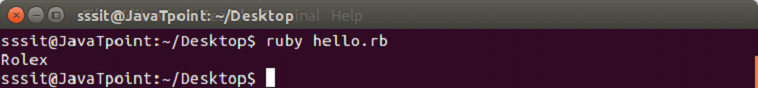
- #!/usr/bin/ruby
- budget = 50000
-
- watch = case budget
- when 100..1000 then "Local"
- when 1000..10000 then "Titan"
- when 5000..30000 then "Fossil"
- when 30000..100000 then "Rolex"
- else "No stock"
- end
-
- puts watch
Output:
Ranges as Intervals
Ranges can also be defined in terms of intervals. Intervals are represented by === case equality operator.
Example:
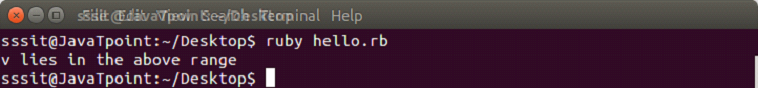
#!/usr/bin/ruby
if (('a'..'z') === 'v')
puts "v lies in the above range"
end
if (('50'..'90') === 99)
puts "z lies in the above range"
endOutput:
Ruby Reverse Range
Ruby reverse range operator does not return any value. If left side value is larger than right side value in a range, no vlaue will be returned.
Example:
- #!/usr/bin/ruby
- puts (5..1).to_a
Nothing will be returned in the output for the above example.
To print a reverse order, you can use reverse method in a normal range as shown below.
Example:
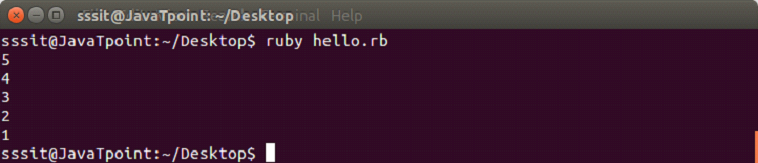
#!/usr/bin/ruby
puts (1..5).to_a.reverseOutput:
Leave a Reply