The Ruby if else statement is used to test condition. There are various types of if statement in Ruby.
- if statement
- if-else statement
- if-else-if (elsif) statement
- ternay (shortened if statement) statement
Ruby if statement
Ruby if statement tests the condition. The if block statement is executed if condition is true.
Syntax:
if (condition)
//code to be executed
end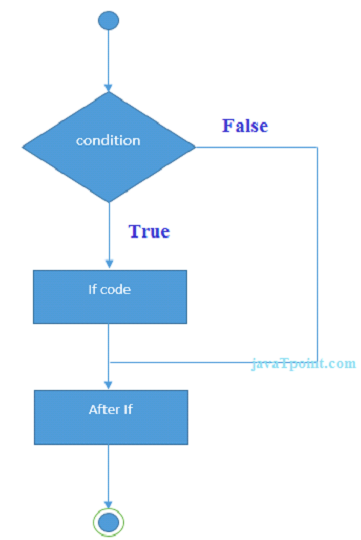
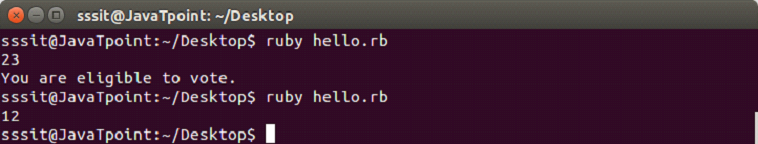
Example:
a = gets.chomp.to_i
if a >= 18
puts "You are eligible to vote."
endOutput:
Ruby if else
Ruby if else statement tests the condition. The if block statement is executed if condition is true otherwise else block statement is executed.
Syntax:
if(condition)
//code if condition is true
else
//code if condition is false
end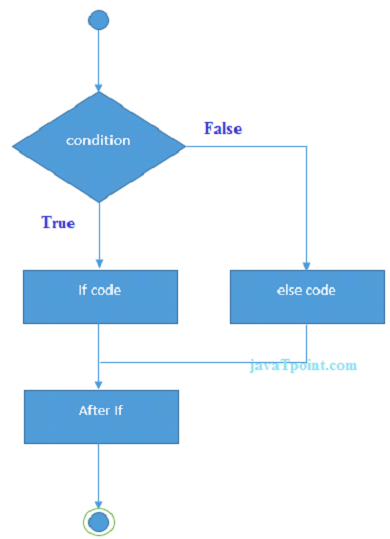
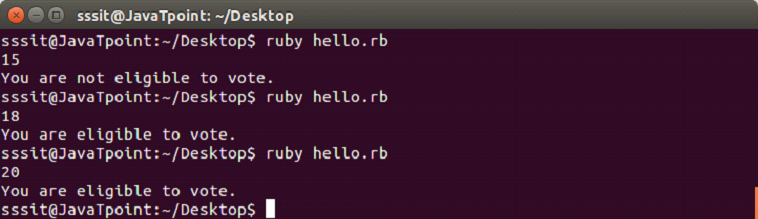
Example:
a = gets.chomp.to_i
if a >= 18
puts "You are eligible to vote."
else
puts "You are not eligible to vote."
endOutput:
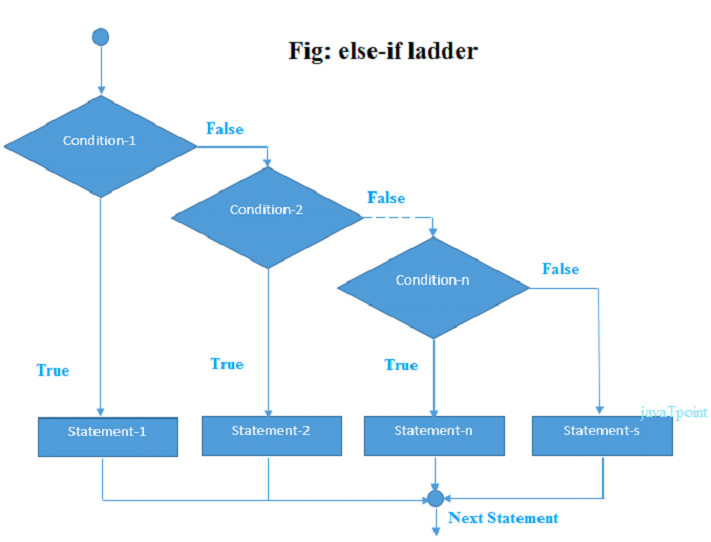
Ruby if else if (elsif)
Ruby if else if statement tests the condition. The if block statement is executed if condition is true otherwise else block statement is executed.
- if(condition1)
- //code to be executed if condition1is true
- elsif (condition2)
- //code to be executed if condition2 is true
- else (condition3)
- //code to be executed if condition3 is true
- end
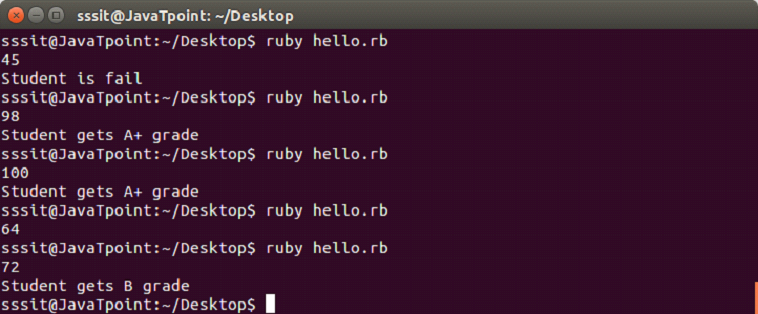
Example:
a = gets.chomp.to_i
if a <50
puts "Student is fail"
elsif a >= 50 && a <= 60
puts "Student gets D grade"
elsif a >= 70 && a <= 80
puts "Student gets B grade"
elsif a >= 80 && a <= 90
puts "Student gets A grade"
elsif a >= 90 && a <= 100
puts "Student gets A+ grade"
endOutput:
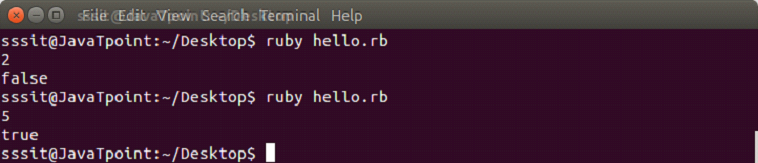
Ruby ternary Statement
In Ruby ternary statement, the if statement is shortened. First it evaluats an expression for true or false value then execute one of the statements.
Syntax:
- test-expression ? if–true-expression : if–false-expression
Example:
var = gets.chomp.to_i;
a = (var > 3 ? true : false);
puts aOutput:
Leave a Reply